Towards differentiation of Panax vietnamensis and Panax vietnamensis var. fuscidiscus by UPLC-QTOF-MS.
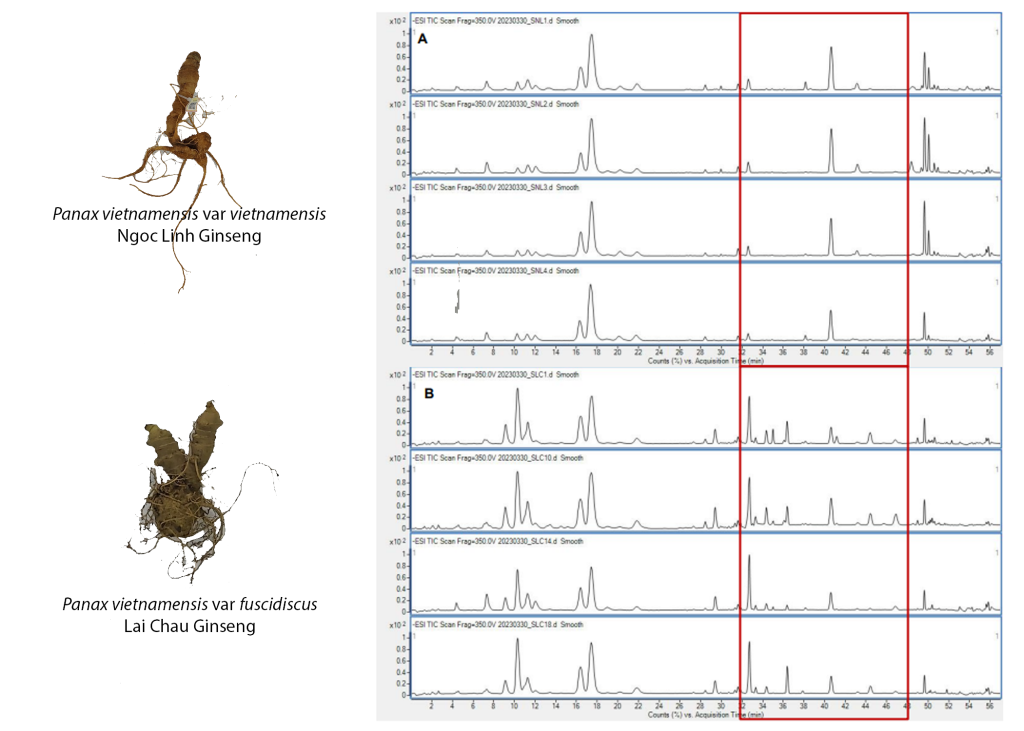
Vietnamese ginseng (Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grusvh., Araliaceae - PV) is a high-value medicinal plant of Vietnam. Recently, a new variety of this plant P. vietnamensis var fuscidiscus (PVF), so-called Lai Chau ginseng, was discovered and circulated on the Vietnam market along with PV. In general, PV and PVF rhizomes and roots are preliminarily reported to possess similar saponin composition. However, PV is much more expensive than PVF due to the higher regard of the consumer, which consequently leads to the inattentive misuse or intentional adulteration of PV by PVF. In this study, an UPLC-ToF-MS method was developed to distinguish PV and PVF based on their saponin profiles. The UPLC qualitative result showed that the saponin constituent of PVF is more complex than that of PV. The major differences in the chromatogram of PV and PVF extracts are the peaks eluted from 32-48 min. Vina-ginsenoside-R2 (9), chikusetsusaponin L8 (10), and N-R4 (12) are characterized for PVF, while N-Fa (13), quinquenoside R1 (16), and pseudoginsenoside Rs1 (19) are specialized for PV. The preliminary quantitative determination result showed that the content of majonoside-R2, ginsenoside Rg1, ginsenoside Rb1, and ginsenoside Rd in PV is higher than those in PVF. In contrast, the content of majonoside-R1 and vina-ginsenoside R2 in PVF is significantly higher than those in PV. The developed method could be used as an effective method to distinguish PV and PVF.






